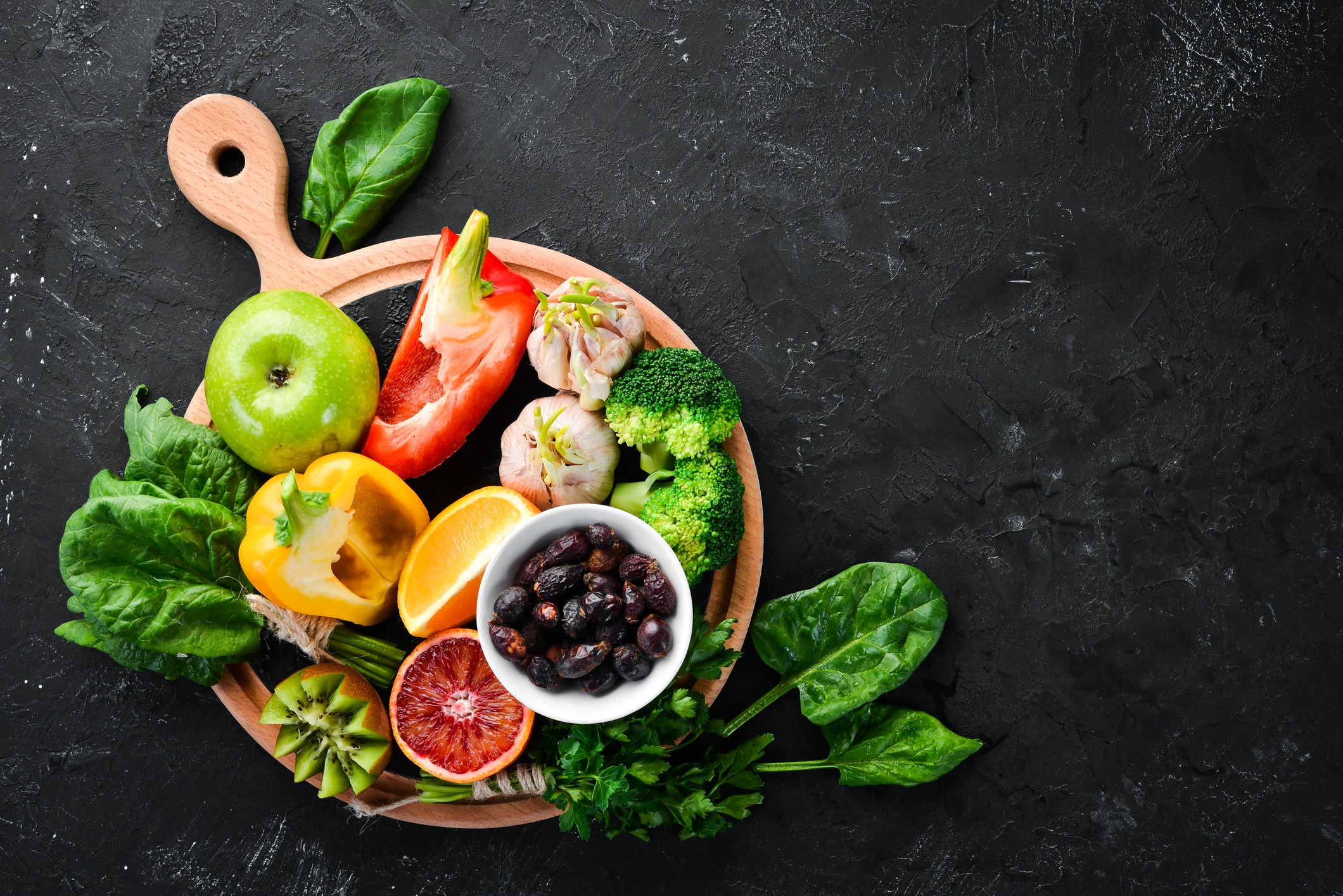
Cold and flu season is here! This year may be more significant in terms of illness because we have gone through a year-plus of isolation and have not had many exposures to infections and viruses. The Institute for Functional Medicine explains that Vitamin C can play a crucial role in boosting not only your immune function but also in protein metabolism, wound healing, gene expression, and collagen production. Vitamin C is also an antioxidant, which may slow or prevent cellular damage, and helps facilitate various important chemical reactions in the body. Higher levels of Vitamin C have been associated with decreased incidence of stroke, hypertension, and coronary artery disease, making it a great, all-around nutrient to maintain whole-body health.
Unlike other animals, humans don’t have the ability to synthesize Vitamin C. Instead, we must acquire it from our diet. Fruits and vegetables contain the most naturally occurring vitamin C of all food sources. Some fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals and supplements also contain Vitamin C. Vitamin C is heat-sensitive, so eating fruits and vegetables, either raw or lightly steamed, is recommended to preserve the most nutrients. Fortunately, Vitamin C deficiency is rare as long as fruits and vegetables are regularly included in the diet. Individuals who smoke or eat few fruits and vegetables may be at an increased risk for vitamin C insufficiency. Below, we’re sharing the best sources of Vitamin C so you can be sure you’re getting your recommended daily allowance for a healthier cold and flu season!
The Recommended Daily Allowance for Vitamin C is as follows:
females (19+) 75mg per day
with pregnancy (19+) 85 mg per day
lactating ages (19+) 120 mg per day
males (19+) 90 mg per day
Vitamin C contents in food:
Food mg of Vitamin C
red sweet pepper (1/2 raw) 95
strawberries (1 cup) 85
orange (1 medium) 70
kiwi (1 medium) 65
sweet green pepper (1/2 raw) 60
broccoli (1/2 cup raw) 50
Brussel sprouts 45
grapefruit (1/2 medium) 44
tomato juice (3/4 cup) 33
cantaloupe (1/2 cup) 30
cabbage (1/2 cup cooked) 28
cauliflower (1/2 cup raw) 26
References:
https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/vitamin-C
Institute for Functional Medicine Toolkit
Written by Stephanie Muntzer, MPT, PYT, RYT200, CPI, SFMA, FMSc